Are you confused about reflow soldering or how to solder surface mount components onto PCBs? While just starting in electronics assembling or looking to enhance your knowledge, understanding this process is essential for creating reliable connections.
We will guide you through all the steps, from gently heating the PCB to cooling. We will also explain the equipment required and key factors in choosing solder paste.
By the end, you will be confident to move between tasks involving reflow soldering and learn how to assemble your PCBs quickly without any errors.
So, let’s begin.
What is Reflow Soldering
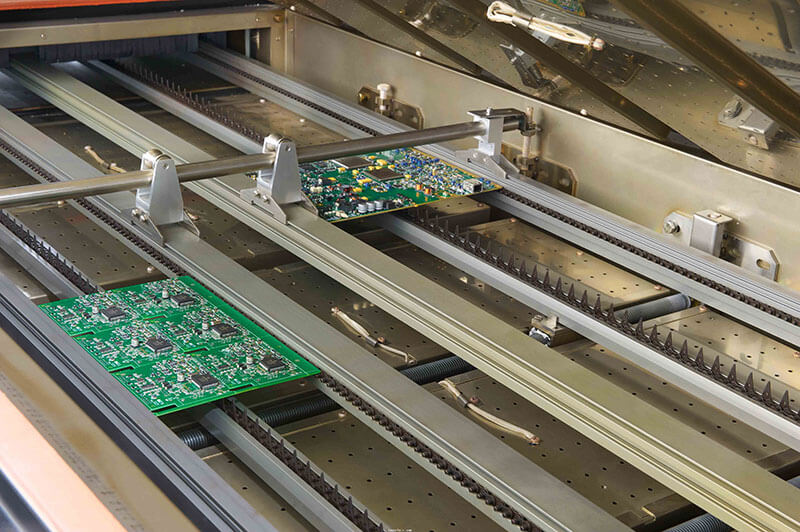

Reflow soldering is an automatic procedure that is very significant for attaching surface mount components on the surface of the printed circuit board.
This method accelerates the soldering process through its process equipment, reflow, in the chamber where solder paste is applied over SMC before being applied and then heated, causing the paste to melt and provide electrical connections between SMC and the pads’ electronic components.
Surface Mount Technology has tremendously changed PCB assembly by the capability to place components right into the surface of the board instead of sending leads through holes.
This miniaturized design improves PCB functionality and space efficiency in electronics. SMT uses soldering to create electrical connections, whereby solder paste—comprising flux and tiny solder particles—is applied on pads positioned on a PCB before mounting components.
Subsequently, the reflow soldering method melts this paste and forms the rugged and durable joints between these components and the PCB.
Let’s discuss the reflow soldering process in detail.
The Reflow Soldering Process
Reflow soldering is indeed a very complex process, which always consists of some stages that are necessary for the reliable assembly of surface mount components onto printed circuit boards.
These are the steps that you need to know:
1. Preheat
The PCB is slightly heated during this preheating stage to drive off moisture from the board and prepare the components to withstand the initial temperature shock during soldering.
This is very important because it protects against thermal shock to the components in the later reflow stage.
2. Soak
Once preheated, the PCB enters the soak phase, where the temperature is constant. This is a critical temperature for uniformity across the whole board. It conditions the solder paste for subsequent reflow and components.
3. Reflow
At this stage, reflow soldering is at its peak, and the temperature is higher, melting the solder paste applied at the pads of the PCB. The good melting of the solder paste allows better electrical connectivity between the SMCs and the PCB.
4. Cooling
After reflow, the tempered cooling of the PCB will permit the solder joints to harden. Decreasing the temperature stepwise will allow these interconnections to cool properly into shape, holding the SMCs into position and, therefore securing general reliability in the PCB assembly.
Each of the steps involved is carefully controlled to make the reflow soldering process aid in producing the best results, hence making electronics solid and functional that are fabricated with SMT.
Reflow Soldering Equipment
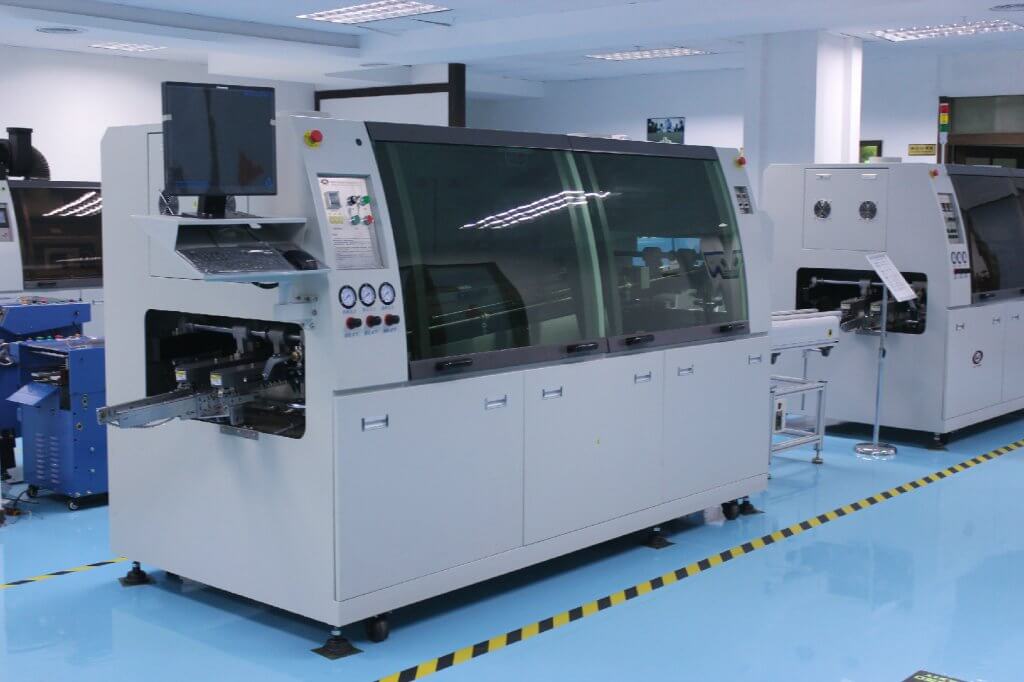

Reflow soldering is the process that relies on special equipment to achieve specific, efficient soldering of SMCs onto printed circuit boards.
The following are the main tools that are used throughout this process:
1. Reflow Oven
A crucial component of reflow soldering, the reflow oven is designed to heat the PCB according to a predefined thermal profile. Typically conveyorized, these ovens ensure consistent heating across the PCB, crucial for achieving reliable solder joints.
2. Solder Paste Dispenser
It dispenses the right amount of solder paste onto designated pads on the PCB. This equipment is very critical for dispensing the correct amount of solder paste to the pad of this printed circuit board and ensures right coverage and distribution before reflow.
3. Pick-and-Place Machine
It plays a vital role in automated assembly—that pick-and-place machine accurately positions SMT components onto solder paste deposits on the PCB—necessary for properly aligned components and eventual formation of appropriate solder joints.
4. Cleaning Equipment
Cleaning equipment removes flux residue on the PCB after the soldering process. Flux residues may have some sort of effect on the long-term reliability of the PCB, hence the need for careful cleaning to ensure the board meets quality standards, thus increasing its lifespan.
These are specialized tools used in the reflow soldering process that make it possible to produce PCB assemblies of high quality with consistent and dependable solder joints.
Now you know the basics of reflow soldering and it’s process. The most important thing in this whole process is the selection of solder paste.
Let’s discuss this in detail.
Solder Paste Selection
Choosing the right solder paste is crucial for successful reflow soldering, as it directly impacts the quality and reliability of solder joints on PCBs.
Importance of Solder Paste Selection
Solder paste acts as a medium for electrical connections between the Surface Mount Components pad during Reflow Soldering.
A number of important factors underlie this selection process:
- Alloy Composition:The choice between lead-free and leaded solder paste will be led by any environmental regulations or applications with a need. Lead is considered bad for the environment, so lead-free should be used, but the rules change for some applications.
- Melting Point:The melting point of any solder paste must be matched with the given reflow profile so that it melts homogenously to give strong solder joints without overheating the components.
- Viscosity:Optimal viscosity ensures the solder paste can be accurately dispensed and remains stable during storage and application. It should flow easily onto PCB pads without excessive dripping.
Careful consideration of these factors ensures that the solder paste used in reflow soldering matches the specific needs of the PCB assembly process, resulting in reliable electrical connections and high-quality manufacturing outcomes.
Advantages and Challenges of Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering provides several advantages for modern electronics manufacturing, but it similarly offers unique challenges that must be managed effectively.
Advantages:
- High speed and high efficiency: Among the fastest processes, reflow soldering is quick and adequate for large volumes of PCB assembly at high speed, considering meeting or keeping up with the production demand.
- Consistent and Repeatable Solder Joint Formation: The automatic nature of reflow soldering permits the formation of repeatable solder joints across various boards while drastically lowering the variability and instances of defects in a general view.
- Suitable for Small and Intricate SMT Components:It supports small and intricate SMCs, making compact designs in PCBs possible without compromising reliability.
Challenges:
- Specialized Equipment and Process Controls Required:Effective reflow soldering requires specialized ovens, solder paste dispensers, and precise process control. This equipment tends to be quite costly, and it requires experience to run the equipment effectively.
- Results: Defects can occur if the profiles are not optimized because of temperature-profile variations during reflow. Such temperature variations can produce either solder bridging or turns, causing joint defects. Hence, the optimization of reflow profiles is highly essential in reducing such problems.
These challenges need to be managed in the best possible way while leveraging the advantages that reflow soldering has for maximum productivity and the highest possible quality PCB assemblies in electronics manufacturing.
Troubleshooting Reflow Soldering Defects
Although reflow soldering is a very efficient process, it can sometimes create defects in the integrity of a PCB assembly.
Understanding these common issues and their causes is crucial for doing effective troubleshooting to ensure high-quality production.
Common Reflow Soldering Defects:
- Bridging
Excessive solder paste or a non-optimally designed stencil may result in the creation of solder bridges, connecting the neighboring two or more pads on the PCB.
The volume of solder paste and the design of stencils should be adjusted with a view to controlling deposition such that the spacing between pads is appropriate.
- Voids
Air pockets trapped within the solder joint during reflow can reduce electrical conductivity and mechanical strength.
Reflow profile optimization — good outgassing of flux during solder reflow, with wetting, to avoid void formation.
- Tombstoning
Components that should lie down on the PCB can sometimes, because of uneven heating or intermittent solder paste application, stand up vertically (tombstone).
Uniform heating across the PCB should be observed during reflow. The correct placement of the components would be determined by using a pick-and-place machine.
- Opens
Insufficient solder paste application or poor wetting between component leads and PCB pads can result in incomplete solder joints, leading to open connections.
Verify solder paste volume and placement accuracy. Adjust solder paste dispensing parameters and inspect for proper wetting during reflow.
Pointing out and rectifying these common defects in reflow soldering can help to improve yield rate, reliability of products, and quality consistency in assembling printed circuit boards.
Final Thoughts
Reflow soldering is essential for modern electronics, offering efficient assembly of surface mount components onto printed circuit boards. This guide has covered everything about the reflow soldering process equipment needed and techniques to overcome challenges.
By mastering these techniques and troubleshooting common issues like bridging and tombstoning, manufacturers can ensure reliable PCB assembly. This approach not only enhances product quality but also supports innovation in electronics manufacturing.