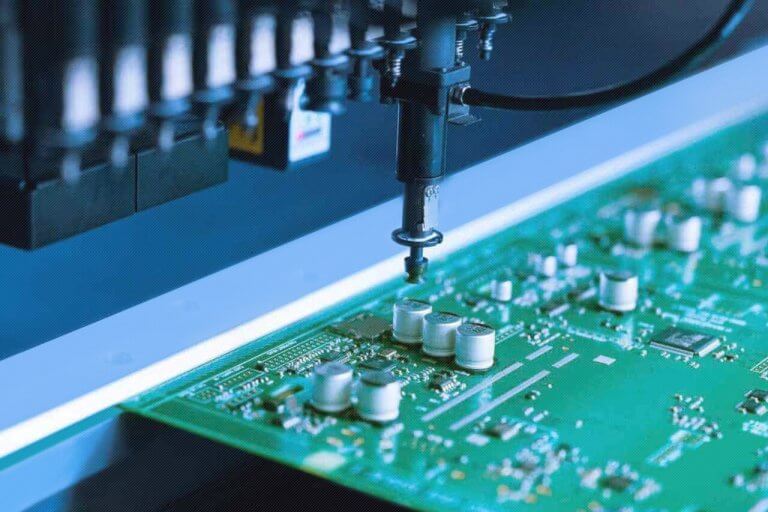
The demand for high-quality, dependable electronics is stronger than ever. But keeping PCB assembly consistent is difficult. Issues like shipping delays, poor quality, and unclear communication can break your schedule and disrupt production. Choosing China for PCB assembly is important because you’re not just hiring a supplier—you’re working with a partner focused on quality, quick delivery, and clear teamwork.
Why choose China? First, its manufacturing system is strong. Full supply chains here reduce material shortages. Automated lines ensure accuracy, even for big orders. Local support teams can fix problems quickly. These features help operations run smoothly, whether you’re building medical devices, aerospace systems, or industrial equipment.
Chinese manufacturers also have years of experience with complex PCBs. They use tools like AI for quality checks and 5G for monitoring to meet strict standards. Being near component hubs reduces shipping delays. This allows them to adjust to design changes or handle rush orders. In today’s world, where electronics need both speed and reliability, China’s PCB assembly helps you improve product quality and reach the market faster.
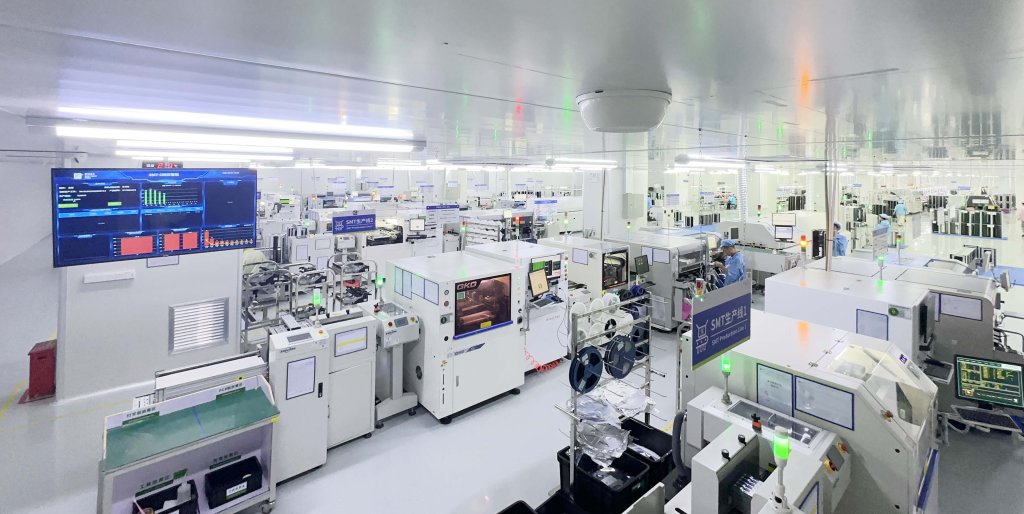

Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Overview
Before diving into the assembly, let’s ground ourselves in the foundation: the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). This is more than just a flat piece of material; it’s the bedrock upon which the entire electronic functionality of a device is built.
Definition: The Core of Modern Electronics
A PCB serves as the physical platform and electrical backbone for electronic components. It’s typically a flat board made from non-conductive material, such as fiberglass, with conductive pathways, or traces, etched or printed onto its surface. These traces connect various components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs), transforming a collection of individual parts into a functioning circuit. The PCB itself is the bare board; PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to the board *after* all components have been soldered onto it.
PCB Assembly Process Types
The magic of transforming a bare PCB into a functional PCBA happens through sophisticated assembly processes. The choice of technique hinges on factors like component type, production volume, and cost considerations.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
SMT Assembly is the dominant force in modern electronics assembly. Components designed for SMT (Surface Mount Devices, or SMDs) have small leads or no leads at all and are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB. The process typically involves applying solder paste to the board, precisely placing components using high-speed pick-and-place machines, and then passing the board through a reflow oven to melt the solder and create permanent connections. SMT allows for higher component density, smaller board sizes, and is highly automated, making it ideal for mass production.
Through-Hole Technology (THT)
An older but still relevant technology, THT involves inserting components with leads through holes drilled in the PCB. These leads are then soldered to pads on the opposite side of the board, often using a wave soldering process for efficiency or manual soldering for smaller batches. THT components create stronger mechanical bonds than SMDs, making them suitable for larger components like connectors and transformers, or in applications subject to mechanical stress.
Mixed Technology
Many modern PCBAs utilize a combination of SMT and THT, known as mixed technology. This approach leverages the density and speed of SMT for most components, while employing THT for those requiring greater mechanical strength or specific electrical properties. This hybrid approach offers design flexibility and optimizes for both performance and durability.
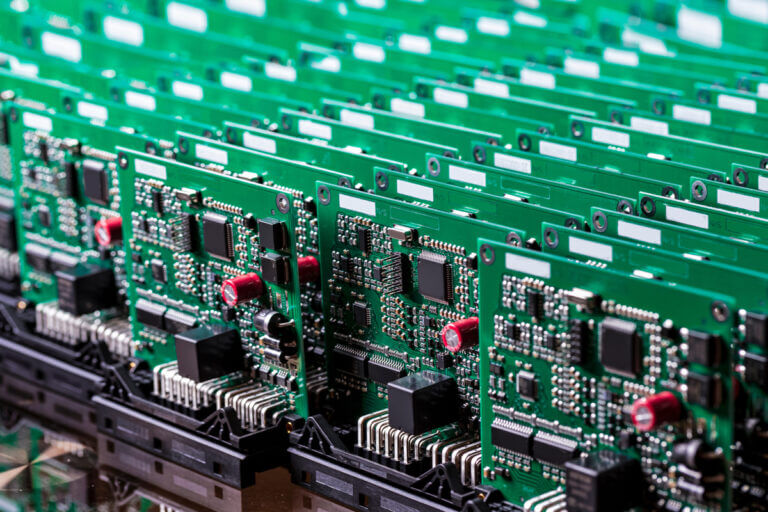
China's 10 Core Advantages in PCB Assembly
China’s ascent in the PCB assembly world isn’t accidental. It’s built on a formidable combination of scale, infrastructure, cost-efficiency, and technological prowess. Let’s dissect the ten pillars supporting its global leadership.
Unrivaled Global Industrial Scale
A Seamless and Hyper-Efficient Supply Chain Ecosystem
The country boasts an incredibly mature and integrated supply chain. Key raw materials like copper foil and copper-clad laminates are largely sourced locally. Furthermore, industrial clusters in regions like the Pearl River Delta and Yangtze River Delta have cultivated an environment where materials and components can often be sourced and delivered within a 24-hour window, a testament to their logistical mastery.
Compelling Comprehensive Cost Advantages
Pioneering Advanced Manufacturing & Process Breakthroughs
Chinese PCB assembly isn’t just about volume; it’s increasingly about sophistication. Manufacturers are adept at producing high-complexity boards, including high-layer-count (e.g., up to 40 layers) PCBs, High-Density Interconnect (HDI) boards, and intricate rigid-flex designs. They are also at the forefront of adopting materials and techniques for 5G high-frequency/high-speed applications, focusing on signal integrity optimization.
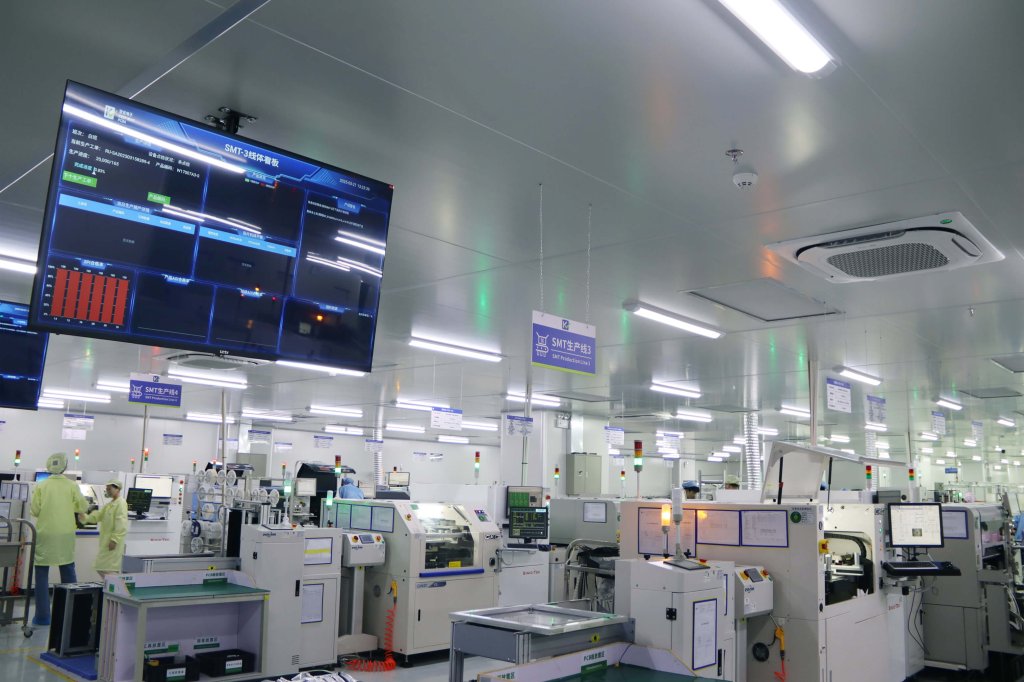

Stringent, World-Class Quality Control Systems
Leading Chinese assemblers adhere to rigorous international quality standards, with certifications like ISO9001 (quality management), ISO14001 (environmental management), RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), and IATF16949 (automotive quality) being commonplace. Many employ advanced inspection methods like Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection, striving for defect rates that meet or exceed global best practices (e.g., aiming for ≤50 parts per million).
Comprehensive One-Stop, Full-Process Service Capability
The rise of “turnkey” solutions is a hallmark of China’s PCBA industry. Many providers offer end-to-end services, from Gerber file design review and component procurement to assembly, testing, and final shipment. This integrated approach simplifies project management and can significantly shorten lead times, with some offering rapid delivery for small to medium batch orders, often within 7-15 days.
Policy Tailwinds & Supportive Industrial Environment
The Chinese government has actively fostered the growth of its high-tech manufacturing sectors, including electronics. This includes various incentives for high-tech enterprises, such as potential tax relief and R&D tax credits. Furthermore, national pushes towards “green manufacturing” are encouraging the adoption of environmentally friendly processes and materials, aligning with global sustainability trends.
A Mature Ecosystem of Talent and R&D Prowess
Decades of manufacturing experience have cultivated a deep pool of skilled engineers, technicians, and production personnel. Strong collaborations between industry and academic institutions fuel innovation in areas like advanced substrates (e.g., for HBM) and embedded component technologies. Consistent R&D investment by leading companies underpins a steady stream of process improvements and patent innovations.
Globalized Logistics & Resilient Delivery Networks
China’s world-class port infrastructure (e.g., Shenzhen, Shanghai) and extensive global shipping networks ensure efficient delivery worldwide. Options for sea and air freight provide flexibility in balancing cost and speed. Many larger PCBA providers also leverage overseas warehousing and bonded zone facilities to streamline international trade and reduce logistical complexities for their global clientele.
Industrial Resilience in Navigating Trade Dynamics
The Chinese PCB assembly industry has demonstrated remarkable adaptability. In response to evolving global trade landscapes, many companies are diversifying by establishing manufacturing capacities in other regions (e.g., Vietnam, Thailand) while simultaneously strengthening domestic capabilities in core technologies. There’s also a growing focus on expanding exports to emerging markets, showcasing the industry’s dynamic approach to global business.
Evaluating the Investment Value of PCB Assembly in China
For businesses seeking reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality PCB assembly, China presents a compelling value proposition. This isn’t just about short-term gains; it’s about strategic, long-term manufacturing partnerships.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: The Clear Winner
When comparing the comprehensive costs – including materials, labor, overhead, and logistics – China often emerges as more advantageous than many Southeast Asian or Western alternatives, especially when factoring in the sheer scale, efficiency, and technological capabilities available. The ability to rapidly scale production up or down also offers significant financial flexibility.
Risk Mitigation: Stability in a Dynamic World
The maturity of China’s supply chain, its robust infrastructure, and the government’s consistent policy support for the manufacturing sector contribute to a relatively stable and predictable operating environment. While no region is immune to global disruptions, China’s established ecosystem offers a degree of resilience that is crucial for long-term planning and risk management.
Market Opportunities: Riding the Wave of Innovation
China is not just a manufacturing hub but also a massive and rapidly growing market for advanced electronics. Aligning PCB assembly with a region that is at the forefront of burgeoning sectors like 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) provides strategic advantages, including proximity to innovation and rapidly evolving market demands.

Conclusion: China's Irreplaceable Stature in PCB Assembly
China has established an irreplaceable core position in the field of Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). This status is rooted in its deep integration of massive industrial scale, a highly integrated supply chain ecosystem, continuous technological innovation, significant cost advantages, and policy support, forming an industry competitive barrier that is difficult to replicate. From currently dominating the global PCBA market to climbing towards technological frontiers such as advanced semiconductor packaging (e.g., System-in-Package) and high-performance computing substrates in the future, China not only supports the operation of the global electronics industry with its end-to-end advantages but also continuously reshapes the landscape of electronic manufacturing by breaking through technological boundaries. Its irreplaceability in the PCBA sector is being further deepened and consolidated along with industrial upgrading.